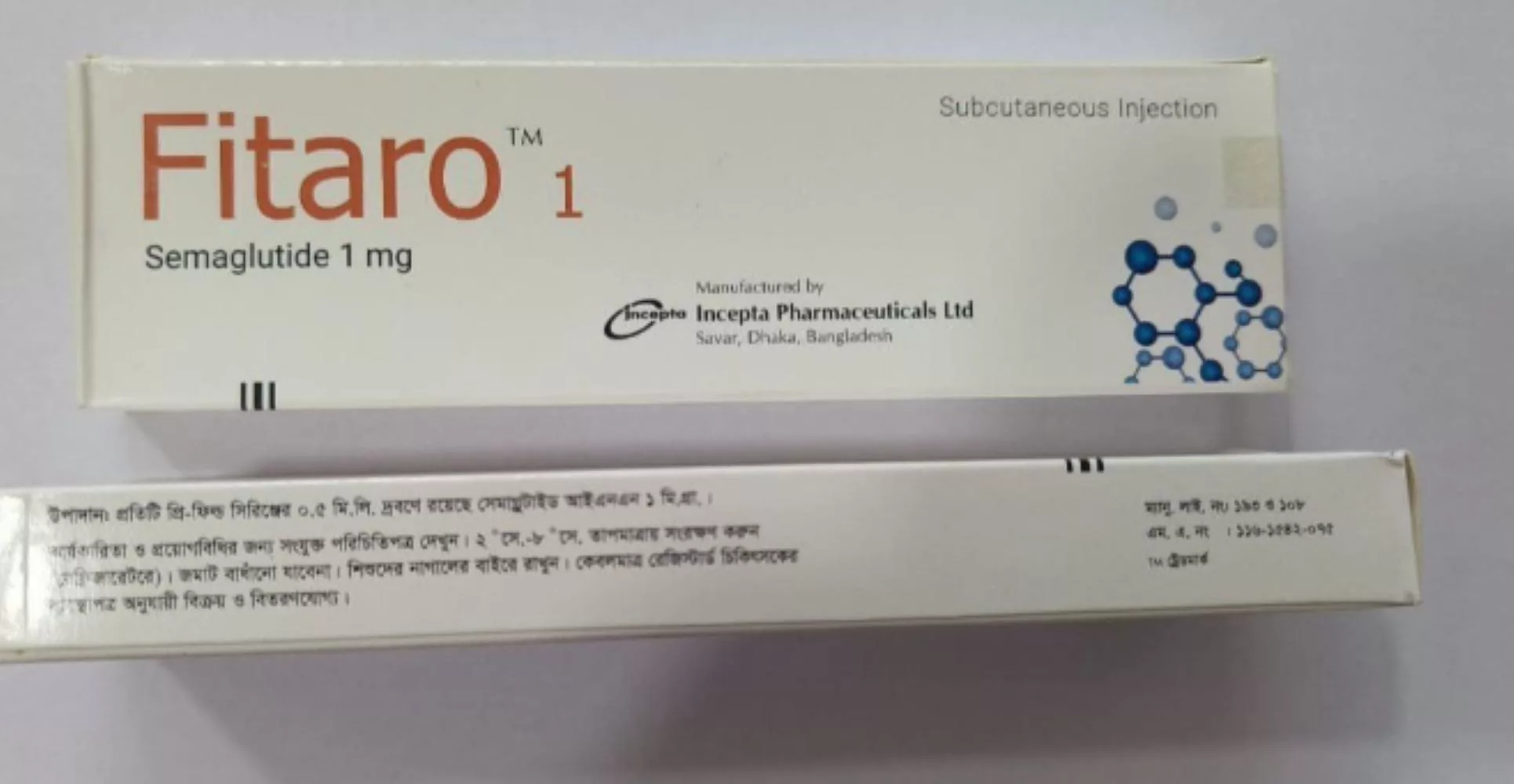
Semaglutide Incepta – Fitaro 1mg worldwide
$400.00 – $4,200.00
| Active ingredient | Semaglutide |
| Producer | Incepta Pharmaceuticals |
| Treatment | Diabetes & Weight loss |
| Packaging | Box |
Uses of Fitaro 1mg Injection
- Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
How does Fitaro 1mg Injection work?
Semaglutide also works by suppressing the release of glucagon (a hormone that raises blood glucose).
Side Effects of Fitaro 1mg Injection
- Complications of diabetic eye disease (retinopathy)
- Feeling sick (nausea) or being sick (vomiting)
- Diarrhea
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Upset stomach or indigestion
- Inflamed stomach (‘gastritis’)
- Stomach ache
- Reflux or heartburn
- Stomach pain
- Bloating of the stomach
- Constipation
- Tiredness
- Less appetite
- Gas (flatulence)
- Increase of pancreatic enzymes (such as lipase and amylase)
Quick Suggestions:
- Take Semaglutide as advised by your physician. It should be taken on an empty stomach. After taking Semaglutide wait at least 30 minutes before having your first meal or drink of the day or taking other oral medicines. Do not stop using this medicine without telling your doctor. Otherwise, your blood sugar levels may raise
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day
- Attend regular health checkups while taking this medicine
- Inform your healthcare provider about all the medications, supplements, and herbal products you are using, as Semaglutide can interact with certain drugs
- Semaglutide is not recommended for use in pregnant or breastfeeding women
Indications:
Semaglutide is used to treat type 2 diabetes in people 18 years and older.
Pharmacology:
GLP-1 Receptor Agonist:
- Binding: Selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor.
- Result: Induces physiological responses associated with GLP-1 receptor activation.
Blood Glucose Reduction:
- Dependency: Reduction occurs in a glucose-dependent manner.
- Insulin Stimulation: Stimulates insulin secretion.
- Glucagon Suppression: Lowers glucagon secretion when blood glucose is elevated.
- Gastric Emptying: Involves a minor delay in gastric emptying.
Hypoglycemia:
- Insulin and Glucagon Regulation: During hypoglycemia, diminishes insulin secretion and does not impair glucagon secretion.
Weight and Fat Reduction:
- Appetite Reduction: Reduces body weight and body fat mass by an overall decrease in appetite.
Dosage
Starting Dose:
- 0.25 mg Semaglutide once weekly for the first 4 weeks subcutaneously.
Dose Escalation Schedule:
- Week 1 through 4: 0.25 mg
- Week 5 through 8: 0.5 mg
- Week 9 through 12: 1 mg
- Week 13 through 16: 1.7 mg
Maintenance Dose:
- Week 17 and onwards: 2.4 mg
Tolerance Considerations:
- If patients do not tolerate a dose during dose escalation, consider delaying dose escalation for 4 weeks.
- If patients do not tolerate the maintenance dose of 2.4 mg, the dose can be temporarily decreased to 1.7 mg once weekly for a maximum of 4 weeks.
- After 4 weeks, increase the dose back to 2.4 mg.
Administration:
- Semaglutide is administered once weekly at any time of the day.
- Can be injected subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
Missed Dose:
- If one dose is missed and the next scheduled dose is more than 2 days away (48 hours), administer Semaglutide as soon as possible.
- If one dose is missed and the next scheduled dose is less than 2 days away (48 hours), do not administer the dose. Resume dosing on the regularly scheduled day of the week.
Interaction
Drug Interactions:
1. Drug-Drug Interactions:
- Potential Interactions: Levothyroxine, warfarin, insulin, bexarotene, and gatifloxacin.
- Action: Inform your doctor about all medications.
2. Drug-Food Interactions:
- Finding: No established food interactions.
- Action: No specific precautions related to food.
3. Drug-Disease Interactions:
- Conditions: Suicidal behavior, thyroid cancer, GI events, hypoglycemia, pancreatitis, retinopathy.
- Action: Be cautious with these conditions; seek medical advice.
Contraindications
Personal or family history of MTC or in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) Known hypersensitivity to semaglutide or any of the product components
Pregnancy & Lactation
Limited Pregnancy Data:
- Data on semaglutide use during pregnancy are limited.
- Animal studies suggest potential fetal risks.
Risk-Benefit Evaluation:
- Use during pregnancy only if benefits justify potential risks.
- Consult with healthcare provider for a thorough risk-benefit assessment.
Discontinuation Before Planned Pregnancy:
- Discontinue semaglutide at least 2 months before planned pregnancy.
- Long washout period considerations.
Clinical Considerations:
- Poorly controlled diabetes during pregnancy increases maternal risks:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Preeclampsia
- Spontaneous abortions
- Preterm delivery
- Stillbirth
- Delivery complications
Fetal Risks with Poorly Controlled Diabetes:
- Increased risk for major birth defects.
- Stillbirth.
- Macrosomia-related morbidity.
Lactation Information:
- No data on semaglutide presence in human milk.
- Effects on breastfed infants and milk production unknown.
- In lactating rats, semaglutide was detected in milk at 3- to 12-fold lower levels than in maternal plasma.
Clinical Guidance:
- Pregnancy: Individualized risk-benefit assessment crucial.
- Discontinuation: Plan to discontinue well in advance of a planned pregnancy.
- Lactation: Lack of data; consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Precautions & Warnings
- Avoid if allergic to any components. Inform your doctor about any allergic reactions.
- Changes in vision, diabetic retinopathy. Report eye problems to your doctor during treatment.
- Stay hydrated, especially with kidney issues. Consult if concerns arise.
- Ongoing stomach pain may indicate acute pancreatitis. Consult a doctor for persistent stomach pain.
- Avoid alcohol to prevent complications. Reduces the risk of lactic acidosis and other issues.
- Not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers, or those below 18. Contact your doctor if pregnancy occurs.
Storage Conditions
Store your Fitaro 1mg Injection in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Be the first to review “Semaglutide Incepta – Fitaro 1mg worldwide” Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.